
by Denae Luna | Oct 26, 2023 | Digital Marketing
Before making any changes or setting new goals, take the time to review and analyze your digital marketing campaign’s performance over the last year. This analysis should comprehensively examine key performance indicators (KPIs), such as website traffic, conversion rates, click-through rates, return on investment (ROI), and other relevant metrics. Pay special attention to what worked and what didn’t.
Specific steps to consider during this review:
Conversion Path Analysis:
We lead off with conversion path analysis because this is one critical aspect that many digital marketers overlook. Examine the customer journey and conversion funnel. Identify any bottlenecks or drop-off points in the funnel and strategize on how to improve the user experience. Many digital marketers focus on the ad funnel, but it’s vital to do conversion path optimization on your website. You need to A/B landing pages and understand customer behavior once they reach your website before you do any other analysis.
Channel Performance:
Evaluate the performance of different marketing channels (e.g., social media, email, paid advertising). Identify which channels were most effective in driving traffic and conversions. Effectiveness can be an elusive thing for marketing teams to agree upon. Too many teams get locked into last click attribution to conversions by channel. The reality is many attribution models are broken or at least less reliable in the age of cookie depreciation/privacy. The best approach to measuring channel performance is a mix of last click attribution, lift tests, surveys, advanced attribution modeling, and good old fashioned common sense when digging into campaign metrics.
Content and Messaging:
Analyze the content and messaging that resonated with your audience. Which types of content generated the most engagement and conversions? What messaging themes were successful? You might be surprised to find content that worked on one channel may not have necessarily worked on another. Optimize your content and messaging by channel but make sure you keep your main branding theme intact for some level of continuity, especially if you are retargeting across channels.
Audience Insights:
Understand your audience’s behavior and preferences. What segments of your audience performed the best, and which ones need improvement? Is your audience data up to date? Use analytics tools, CRM, and customer feedback to gain insights and cleanse any old data on customers that no longer engage or segments that are no longer profitable.
Competitive Analysis:
Look at your competitors’ digital marketing strategies and assess how your performance compares. Identify areas where you can outperform or differentiate.
Budget Allocation:
Review your budget allocation for various marketing channels and campaigns. Determine whether your spending aligns with the best-performing channels and where adjustments may be needed.
Once you’ve gathered and analyzed this data, you can make informed decisions about how to optimize your digital marketing campaign for the new year. This process sets the foundation for setting new goals, refining your strategy, and identifying areas where improvements are needed.
Thinking about next year’s strategy and haven’t considered programmatic advertising? Read this article before you write off the benefits: https://populationscience.com/dont-have-programmatic-in-your-2024-plan-heres-why-you-should-reconsider/
by Denae Luna | Oct 24, 2023 | Digital Marketing, Programmatic
Integrating programmatic advertising into your paid search and paid social strategy can help you create a more holistic and effective digital advertising approach. Here are steps to integrate programmatic into your paid search and paid social campaigns:
Set Clear Goals and Objectives:
Define specific goals for your integrated strategy, such as increasing brand awareness, driving website traffic, or boosting conversions and deploy it across paid search, paid social, and programmatic. This may sound like common sense, but you would be surprised how many media teams have their paid search, paid social, and programmatic strategy living in silos. You will have the maximum amount of success if all of your channels are in sync.
Data Sharing:
Encourage data sharing and collaboration between your programmatic, paid search, and paid social teams. Sharing insights and findings can lead to more effective cross-channel strategies.
Consistent Messaging:
Ensure that your messaging is consistent across programmatic, paid search, and paid social channels. A unified brand message helps reinforce your brand identity and message to your audience. Maintain a consistent visual style and branding elements in your ad creatives across all channels. This helps create a cohesive and memorable brand experience.
Cross-Channel Retargeting:
Use programmatic advertising to retarget users who have engaged with your paid search or paid social campaigns. Via programmatic campaigns you can greatly increase the number of places you can retarget search and social visitors including display, native, connected TV, and even digital audio. Increasing the number of channels you retarget on will ensure your message stays in front of interested audiences any time they are on a connected device. This will help nurture leads and guide them through the conversion funnel.
Leverage Data from Paid Channels:
Incorporate data from your paid search and paid social campaigns into your programmatic strategy. This can help you identify high-performing keywords for contextual tactics, ad creatives, and audience segments to use in programmatic campaigns.
Custom Audiences and Lookalike Audiences:
Use your website as an aggregator to track visitors from all of your paid media campaigns (search, social, and programmatic). This melting pot of data can be fed back into all channels to find lookalikes across all digital channels. Use
Unified Analytics & Attribution:
Use unified analytics and clearly define how attribution will be handled. This allows you to understand the contribution of each channel to your overall marketing efforts and allocate money across the most effective channels. You might be surprised how difficult this is for marketing teams. As more platforms introduce privacy-friendly defaults attribution is becoming more difficult. Paid search, paid social, and programmatic teams often end up fighting over taking credit for conversions which can cause discontent and more importantly lead to a lack of harmony between teams.
Cross-Channel Budget Allocation:
Determine how to allocate your budget across programmatic, paid search, and paid social based on campaign performance. Consider channel-specific ROI and adjust budgets accordingly.
Adapt to Trends and Changes:
Stay updated on industry trends and changes in advertising platforms to ensure your integrated strategy remains current and aligned with best practices. Programmatic is a constantly evolving area of media buying so it is vital to stay informed about new opportunities to target and reach your target audience.
Integrating programmatic into your paid search and paid social strategy requires careful planning, data sharing, and consistent messaging. When executed well, this approach can help you reach your audience across various touchpoints, improving brand visibility and the overall performance of your digital advertising efforts.
When you’re ready to implement programmatic into your efforts, check out our DSP implementation strategy here: https://populationscience.com/how-to-implement-a-demand-side-platform-dsp/

by Denae Luna | Oct 20, 2023 | Digital Marketing, Programmatic
Hiring a programmatic consultant can offer several advantages for businesses and advertisers looking to navigate the complex world of programmatic advertising. Here are some compelling reasons why you should consider hiring a programmatic consultant:
1. Expertise and Experience:
Programmatic consultants are experts in the field with extensive knowledge and experience in programmatic advertising. They stay up-to-date with industry trends, best practices, and the latest technologies, which can be challenging for in-house teams to maintain. Programmatic hasn’t been around as long as paid search or paid social so finding an expert with a lot of experience can be challenging. It can be even harder to hire a full time, experienced programmatic manager in-house.
2. Strategy Development:
Consultants can help you develop a customized programmatic advertising strategy tailored to your business objectives. They can assess your goals, target audience, and budget to create a plan that maximizes ROI. An experienced consultant can ensure your strategy is efficient, effective, and up to date with the latest tactics.
3. Cost Efficiency:
Consultants can optimize your programmatic campaigns to reduce wasted ad spend. They can help you make data-driven decisions, choose the right supply partners, and implement cost-saving measures.
4. Transparency and Accountability:
Programmatic consultants can improve transparency in your supply chain. Your supply chain is the Supply Side Partners (SSPs) and domains/apps you ultimately place your ads on. They can help you understand where your ad dollars are going and ensure that your campaigns are free from fraudulent activity.
5. Vendor and Technology Selection:
Consultants can guide you in selecting the right technology platforms and supply partners for your specific needs. They can help you negotiate contracts and make informed decisions about which vendors to work with. With so many vendors and traffic partners to choose from, simply knowing which ones you need to work with to achieve your unique goals can save you thousands of dollars per month.
6. Ad Creative and Messaging:
Consultants can provide recommendations for optimizing ad creatives and messaging to improve campaign performance and audience engagement. With so many channels and tactics the smallest nuance in creative can make a huge difference.
7. Data Analysis and Insights:
Consultants can analyze campaign data to extract valuable insights. They can identify trends, audience behaviors, and areas for improvement, helping you refine your advertising strategy and understand the ROI on your programmatic investment.
8. Compliance and Privacy:
With increasing privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, consultants can help ensure that your programmatic advertising practices comply with legal requirements, reducing the risk of fines and legal issues.
9. Adapting to Industry Changes:
The programmatic advertising landscape is constantly evolving. Consultants can help you adapt to changes in technology, regulations, and consumer behavior, ensuring that your campaigns remain effective and leverage the latest tactics.
10. Customized Solutions:
Consultants provide personalized solutions based on your unique business needs and challenges. They can adapt strategies to fit your industry, target audience, and competitive landscape.
11. Time Savings:
Outsourcing programmatic expertise to a consultant allows your internal team to focus on other critical tasks, such as core business functions and overall marketing strategy.
12. Objective Perspective:
Consultants offer an objective viewpoint, free from internal biases or politics. They can provide honest feedback and recommendations without being influenced by organizational dynamics.
13. Measurable Results:
Consultants can establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and regularly report on campaign performance, ensuring that you can track and measure the success of your programmatic efforts.
Overall, hiring a programmatic consultant can be a wise investment for businesses looking to leverage programmatic advertising effectively while minimizing risks and optimizing their advertising budget. Consultants bring expertise, objectivity, and a strategic approach that can lead to improved campaign results and a stronger return on investment.
Let us be a part of your journey. Learn more about how we can take your campaigns to the next level.

by Denae Luna | Oct 20, 2023 | Digital Marketing
Targeting digital ads without using cookies has become increasingly important due to privacy concerns and changes in regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which have limited the use of third-party cookies. Here are some tactics you can use to target digital ads effectively without relying on cookies:
Seller Defined Audiences:
-
-
- Seller Defined Audiences (SDAs) define audiences in a standardized manner allowing sellers (publishers, networks, platforms) to communicate their audience segments consistently and transparently across platforms and channels.
- Retail Networks, Private Marketplace Deals, and buying directly from walled gardens/owned and operated inventory (O&O) are all examples of places where you can leverage SDAs.
Contextual Targeting:
-
-
- Contextual targeting involves placing ads on websites or content that are contextually relevant to the ad’s message. This can be done by analyzing the content of web pages, including keywords, topics, and themes.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms can help automate contextual targeting by understanding the content of web pages.
Behavioral Targeting:
-
-
- Instead of relying on third-party cookies for tracking user behavior, consider using first-party data collected from your own website or app.
- Analyze on-site behavior, such as page views, search queries, and user interactions, to create user profiles and target ads based on user interests and preferences.
Device and IP Address Targeting:
-
-
- You can target ads based on device types (e.g., mobile, desktop) and users’ IP addresses.
- Keep in mind that relying solely on IP addresses may not provide individual-level targeting, as multiple users can share the same IP address.
Contextual Keywords:
-
-
- Utilize keyword targeting to display ads on websites or within content that contains specific keywords relevant to your products or services.
Contextual Experiences:
-
-
- Design ad creatives that are contextually relevant to the content, context, and keywords in which they are displayed. This can improve engagement and reduce the need for precise targeting.
Geolocation Targeting:
-
-
- Use geolocation data to target ads to users based on their physical location. This can be effective for local businesses and events.
Demographic and Behavioral Segmentation:
-
-
- Create audience segments based on demographic information (age, gender, income) and observed online behavior.
- Platforms may offer options for creating custom segments without relying on third-party data.
Retargeting and Remarketing:
-
-
- Continue to use first-party data to retarget or remarket to users who have previously interacted with your website or app.
Partnerships and Influencer Marketing:
-
- Collaborate with influencers or other businesses/publishers that have authority with your target audience(s).
- Top influencers can be expensive, but there are plenty of “micro” influencers out there with small, but mighty followings. In fact, they can often have some of the most loyal engagement. They are also more likely to collaborate with you on creating high impact content.
As the digital advertising landscape continues to evolve, it’s essential to adapt to changing privacy regulations and consumer expectations while still delivering effective and relevant ad campaigns. Combining multiple tactics from the list above can help you achieve your targeting goals while respecting user privacy.
Ready to implement your programmatic strategy? Check out our step-by-step here: https://populationscience.com/how-to-implement-a-demand-side-platform-dsp/

by Denae Luna | Oct 17, 2023 | Digital Marketing, Programmatic
Programmatic Supply Path Optimization (SPO) is a strategy used in digital advertising, particularly in programmatic advertising, to improve the efficiency and transparency of the supply chain. It involves optimizing the path through which digital ads are bought and sold, with the goal of maximizing the value for advertisers while minimizing costs and reducing potential fraud.
SPO is a response to the complexity and opacity often associated with programmatic advertising. In short, SPO is about finding the most direct path at the most affordable price to access quality impressions.
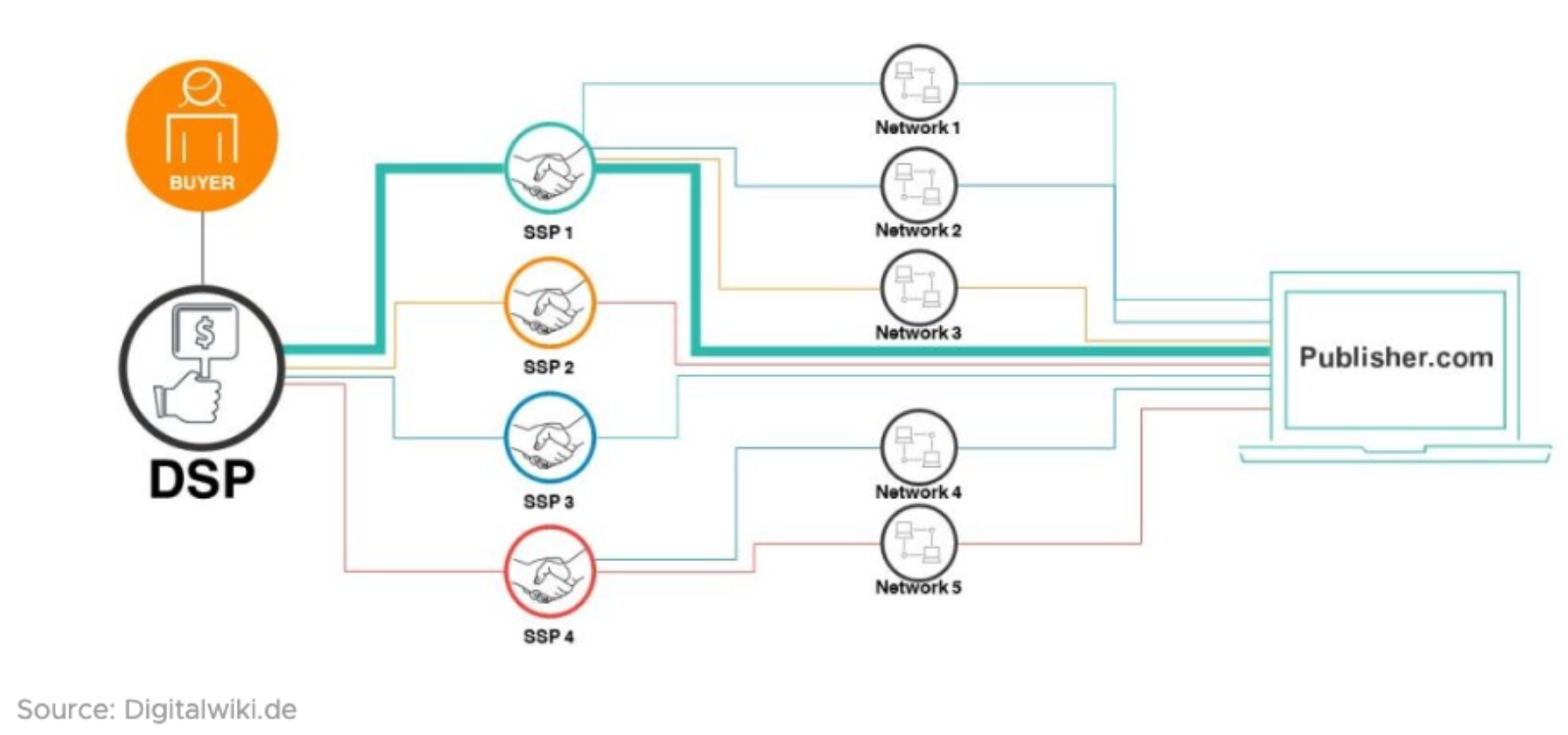
Here are the key components and objectives of Programmatic Supply Path Optimization:
Transparency: SPO aims to increase transparency in the programmatic supply chain. This involves identifying and understanding each step in the supply chain, including the intermediaries and technology platforms involved in the buying and selling of ads.
Cost Reduction: By streamlining the supply chain and reducing unnecessary intermediaries, SPO can help advertisers reduce the fees and costs associated with programmatic advertising. This can lead to improved return on investment (ROI).
Quality and Brand Safety: SPO can help advertisers ensure that their ads are displayed on high-quality, brand-safe websites and apps. It involves choosing the right supply partners and excluding low-quality or potentially harmful inventory sources.
Reducing Ad Fraud: SPO can also help in the detection and prevention of ad fraud. By working with trusted and reputable supply partners, advertisers can minimize the risk of fraudulent ad impressions or clicks.
Data Analysis: Advertisers may use real-time data and technology to make dynamic decisions about which supply paths to use for each impression, optimizing based on factors like price, performance, and quality.
Consolidation: SPO often involves consolidating the number of supply partners or intermediaries involved in a campaign. Fewer intermediaries can lead to a more efficient and cost-effective supply chain.
Relationship Building: Building strong relationships with supply partners is another aspect of SPO. Collaborative partnerships can lead to better communication, trust, and more effective campaign management.
In summary, programmatic supply path optimization is a strategy that advertisers use to make their programmatic advertising campaigns more efficient, transparent, and cost-effective. It involves careful selection of supply partners, data analysis, and ongoing optimization to achieve better results in the complex world of programmatic advertising.
Want some more help making a programmatic decision? Check out our Demand Side Platform Buyer’s Guide: https://populationscience.com/demand-side-platform-buyer-guide/









